Class Solution
- java.lang.Object
-
- g0601_0700.s0684_redundant_connection.Solution
-
public class Solution extends Object
684 - Redundant Connection.Medium
In this problem, a tree is an undirected graph that is connected and has no cycles.
You are given a graph that started as a tree with
nnodes labeled from1ton, with one additional edge added. The added edge has two different vertices chosen from1ton, and was not an edge that already existed. The graph is represented as an arrayedgesof lengthnwhereedges[i] = [ai, bi]indicates that there is an edge between nodesaiandbiin the graph.Return an edge that can be removed so that the resulting graph is a tree of
nnodes. If there are multiple answers, return the answer that occurs last in the input.Example 1:
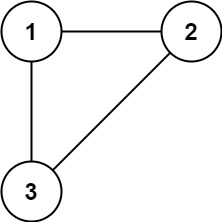
Input: edges = [[1,2],[1,3],[2,3]]
Output: [2,3]
Example 2:
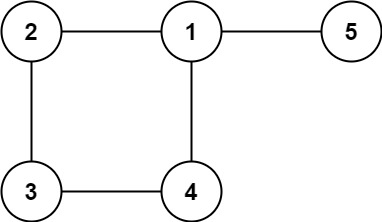
Input: edges = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[1,4],[1,5]]
Output: [1,4]
Constraints:
n == edges.length3 <= n <= 1000edges[i].length == 21 <= ai < bi <= edges.lengthai != bi- There are no repeated edges.
- The given graph is connected.
-
-
Constructor Summary
Constructors Constructor Description Solution()
-
Method Summary
All Methods Instance Methods Concrete Methods Modifier and Type Method Description int[]findRedundantConnection(int[][] edges)
-