Class Solution
- java.lang.Object
-
- g0801_0900.s0835_image_overlap.Solution
-
public class Solution extends Object
835 - Image Overlap.Medium
You are given two images,
img1andimg2, represented as binary, square matrices of sizen x n. A binary matrix has only0s and1s as values.We translate one image however we choose by sliding all the
1bits left, right, up, and/or down any number of units. We then place it on top of the other image. We can then calculate the overlap by counting the number of positions that have a1in both images.Note also that a translation does not include any kind of rotation. Any
1bits that are translated outside of the matrix borders are erased.Return the largest possible overlap.
Example 1:
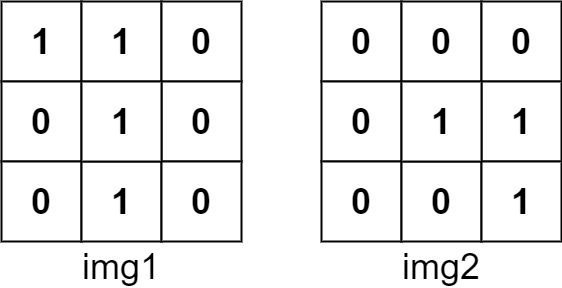
Input: img1 = [[1,1,0],[0,1,0],[0,1,0]], img2 = [[0,0,0],[0,1,1],[0,0,1]]
Output: 3
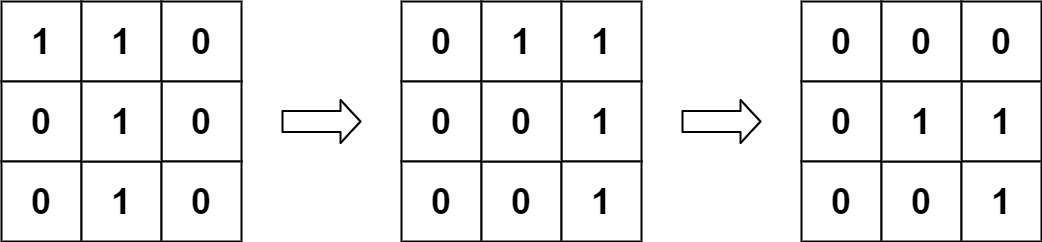
Explanation: We translate img1 to right by 1 unit and down by 1 unit.
 The number of positions that have a 1 in both images is 3 (shown in red).
The number of positions that have a 1 in both images is 3 (shown in red). 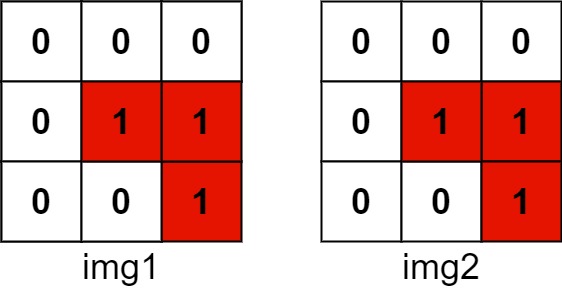
Example 2:
Input: img1 = [[1]], img2 = [[1]]
Output: 1
Example 3:
Input: img1 = [[0]], img2 = [[0]]
Output: 0
Constraints:
n == img1.length == img1[i].lengthn == img2.length == img2[i].length1 <= n <= 30img1[i][j]is either0or1.img2[i][j]is either0or1.
-
-
Constructor Summary
Constructors Constructor Description Solution()
-
Method Summary
All Methods Instance Methods Concrete Methods Modifier and Type Method Description intlargestOverlap(int[][] img1, int[][] img2)
-