Class Skiplist
- java.lang.Object
-
- g1201_1300.s1206_design_skiplist.Skiplist
-
public class Skiplist extends Object
1206 - Design Skiplist.Hard
Design a Skiplist without using any built-in libraries.
A skiplist is a data structure that takes
O(log(n))time to add, erase and search. Comparing with treap and red-black tree which has the same function and performance, the code length of Skiplist can be comparatively short and the idea behind Skiplists is just simple linked lists.For example, we have a Skiplist containing
[30,40,50,60,70,90]and we want to add80and45into it. The Skiplist works this way: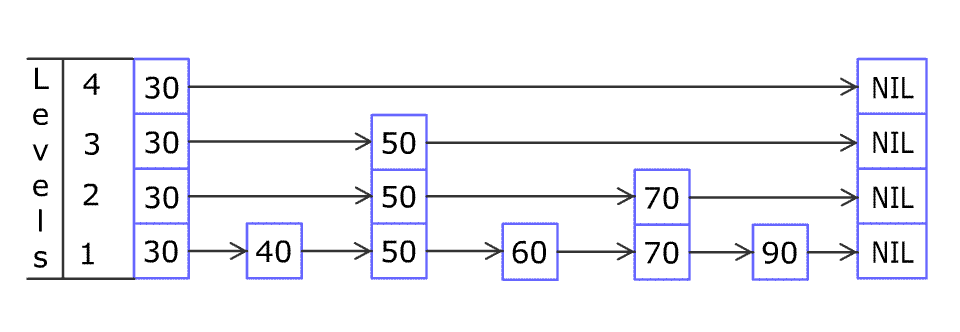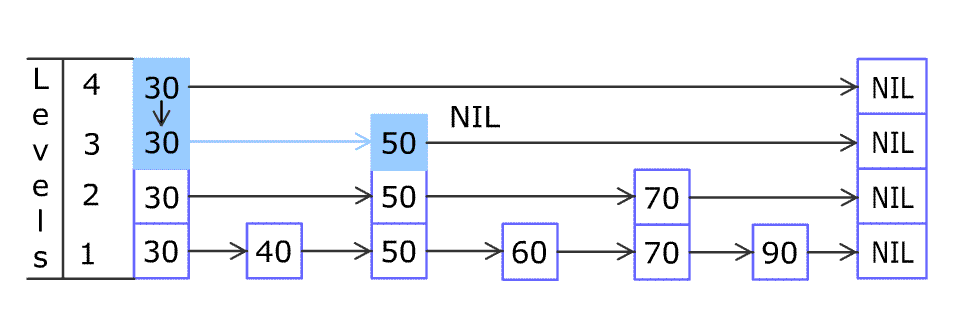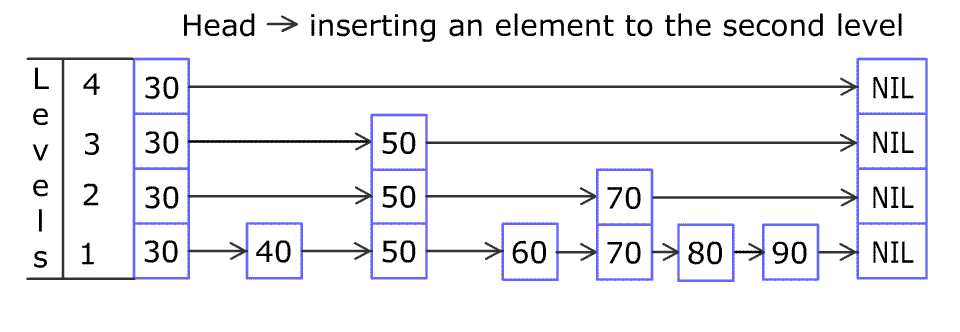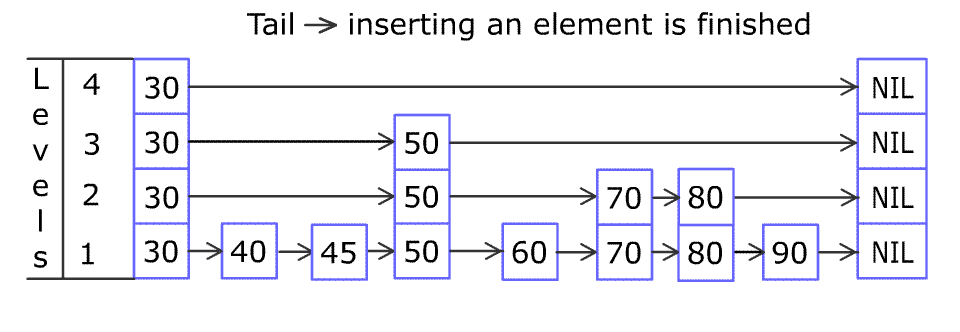
Artyom Kalinin [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia CommonsYou can see there are many layers in the Skiplist. Each layer is a sorted linked list. With the help of the top layers, add, erase and search can be faster than
O(n). It can be proven that the average time complexity for each operation isO(log(n))and space complexity isO(n).See more about Skiplist: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Skip_list
Implement the
Skiplistclass:Skiplist()Initializes the object of the skiplist.bool search(int target)Returnstrueif the integertargetexists in the Skiplist orfalseotherwise.void add(int num)Inserts the valuenuminto the SkipList.bool erase(int num)Removes the valuenumfrom the Skiplist and returnstrue. Ifnumdoes not exist in the Skiplist, do nothing and returnfalse. If there exist multiplenumvalues, removing any one of them is fine.
Note that duplicates may exist in the Skiplist, your code needs to handle this situation.
Example 1:
Input
[“Skiplist”, “add”, “add”, “add”, “search”, “add”, “search”, “erase”, “erase”, “search”]
[ [], [1], [2], [3], [0], [4], [1], [0], [1], [1]]
Output: [null, null, null, null, false, null, true, false, true, false]
Explanation:
Skiplist skiplist = new Skiplist(); skiplist.add(1); skiplist.add(2); skiplist.add(3); skiplist.search(0); // return False skiplist.add(4); skiplist.search(1); // return True skiplist.erase(0); // return False, 0 is not in skiplist. skiplist.erase(1); // return True skiplist.search(1); // return False, 1 has already been erased.Constraints:
0 <= num, target <= 2 * 104- At most
5 * 104calls will be made tosearch,add, anderase.
-
-
Method Summary
All Methods Instance Methods Concrete Methods Modifier and Type Method Description voidadd(int num)booleanerase(int num)booleansearch(int target)
-