Class Solution
java.lang.Object
g1501_1600.s1582_special_positions_in_a_binary_matrix.Solution
1582 - Special Positions in a Binary Matrix\.
Easy
Given an `m x n` binary matrix `mat`, return _the number of special positions in_ `mat`_._
A position `(i, j)` is called **special** if `mat[i][j] == 1` and all other elements in row `i` and column `j` are `0` (rows and columns are **0-indexed** ).
**Example 1:**
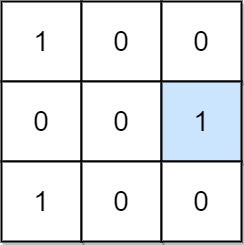
**Input:** mat = \[\[1,0,0],[0,0,1],[1,0,0]]
**Output:** 1
**Explanation:** (1, 2) is a special position because mat[1][2] == 1 and all other elements in row 1 and column 2 are 0.
**Example 2:**
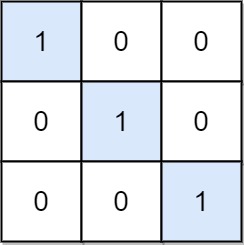
**Input:** mat = \[\[1,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,1]]
**Output:** 3
**Explanation:** (0, 0), (1, 1) and (2, 2) are special positions.
**Constraints:**
* `m == mat.length`
* `n == mat[i].length`
* `1 <= m, n <= 100`
* `mat[i][j]` is either `0` or `1`.
-
Constructor Summary
Constructors -
Method Summary
-
Constructor Details
-
Solution
public Solution()
-
-
Method Details
-
numSpecial
public int numSpecial(int[][] mat)
-