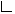 gate.creole.annic.apache.lucene.search.Query
gate.creole.annic.apache.lucene.search.Query
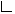 gate.creole.annic.apache.lucene.search.PhraseQuery
gate.creole.annic.apache.lucene.search.PhraseQuery
|
||||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | |||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | |||||||||
java.lang.Objectgate.creole.annic.apache.lucene.search.Query
gate.creole.annic.apache.lucene.search.PhraseQuery
public class PhraseQuery
A Query that matches documents containing a particular sequence of terms.
This may be combined with other terms with a BooleanQuery.
| Constructor Summary | |
|---|---|
PhraseQuery()
Constructs an empty phrase query. |
|
| Method Summary | |
|---|---|
void |
add(Term term)
|
void |
add(Term term,
Integer position,
boolean considerAsATerm)
Adds a term to the end of the query phrase. |
protected Weight |
createWeight(Searcher searcher)
Expert: Constructs an appropriate Weight implementation for this query. |
boolean |
equals(Object o)
Returns true iff o is equal to this. |
int |
getSlop()
Returns the slop. |
Term[] |
getTerms()
Returns the set of terms in this phrase. |
int |
hashCode()
Returns a hash code value for this object. |
void |
setSlop(int s)
Sets the number of other words permitted between words in query phrase. |
void |
setTotalTerms(int totalTerms)
|
String |
toString(String f)
Prints a user-readable version of this query. |
| Methods inherited from class gate.creole.annic.apache.lucene.search.Query |
|---|
clone, combine, getBoost, getSimilarity, mergeBooleanQueries, rewrite, setBoost, toString, weight |
| Methods inherited from class java.lang.Object |
|---|
finalize, getClass, notify, notifyAll, wait, wait, wait |
| Constructor Detail |
|---|
public PhraseQuery()
| Method Detail |
|---|
public void setSlop(int s)
WITHIN or NEAR operator.
The slop is in fact an edit-distance, where the units correspond to moves of terms in the query phrase out of position. For example, to switch the order of two words requires two moves (the first move places the words atop one another), so to permit re-orderings of phrases, the slop must be at least two.
More exact matches are scored higher than sloppier matches, thus search results are sorted by exactness.
The slop is zero by default, requiring exact matches.
public int getSlop()
public void add(Term term,
Integer position,
boolean considerAsATerm)
public void setTotalTerms(int totalTerms)
public void add(Term term)
public Term[] getTerms()
protected Weight createWeight(Searcher searcher)
QueryOnly implemented by primitive queries, which re-write to themselves.
createWeight in class Querypublic String toString(String f)
toString in class Querypublic boolean equals(Object o)
o is equal to this.
equals in class Objectpublic int hashCode()
hashCode in class Object
|
||||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | |||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | |||||||||